Xavier University was chosen as one of ten Colleges and Universities to receive a Building Infrastructure Leading to Diversity (BUILD) award. These awards are part of a larger initiative by the NIH: Enhancing the Diversity of the NIH-funded workforce. Xavier University has developed a program called Project PATHWAYS, which includes several components targeting students, faculty, and several non-academic centers on campus.
The NIH has recently released this funding opportunity announcement (FOA) for institutions that are interested in taking the Diversity Program Consortium (DPC) scientific approach to understanding the effectiveness of biomedical research training, mentoring, or research capacity building interventions aimed at enhancing diversity in the biomedical research workforce. This FOA solicits applications from institutions not currently part of the Common Fund Enhancing Diversity in the Biomedical Research Workforce initiative, also known as the DPC, to expand the national impact of the program. As Xavier University of Louisiana (Xavier) is a member of the DPC, the initiatives developed under Project Pathways, the BUILD (Building Infrastructure Leading to Diversity) program at Xavier can be disseminated to other eligible institutions under this new funding mechanism.
DPC Dissemination and Translation Awards (DPC DaTA): This initiative provides an opportunity for institutions not currently part of the DPC to apply for funding to take a rigorous scientific approach to understand the effectiveness of a biomedical research training, mentoring, or research capacity building intervention by employing DPC experimental methods. (RFA-RM-19-003)
Please contact Dr. Maryam Foroozesh (mforooze@xula.edu) if you are interested in such collaborations.
-

Fluorescence-Based Molecular Switches for piR 1245 Detection
Racquel Amadi, Jessica Anderson, Najah Dixon, and Mehnaaz F. Ali
Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) is a type of non-coding small nucleotide sequence that was recently discovered. PiRNA serves as modulators of transcription and plays a key role in tumorigenesis. Our lab has been working with piR 1245, which serves as a clinical biomarker for colon cancer since it is upregulated in the disease state. Previous experiments have shown the design of a sensing mechanism for these short nucleotide sequences using aptamers which are single stranded sequences of DNA or RNA which can fold into complex threedimensional shapes and form binding pockets and cavities. In our previous experiment, our lab used fluorescence to demonstrate proof of concept that the introduction and hybridization of the piR1245 target sequence led to the displacement of the fluorophore-linked signaling sequences from the aptamer and that the signals were amplified using dual probes. Our goal is to use fluorophore based aptamer sensors for piRNA and conjugate the signaling sequences with flavin adenine dinucleotide (a redox trigger of the enzyme Glucose oxidase), rather than FAM (which is a fluorophore similar to FITC). The results will be detected using an apo-Glucose oxidase reactivation assay and provide enzymatic amplification in signaling.
-

Investigating the effects of neurokinin antagonists on reducing nicotine consumption
Kyla Bongay-Williams
has surged with adolescents and adults. Very much like other tobacco products, e-cigarettes are very addictive because they contain nicotine. Nicotine use in adolescence is an issue because it affects brain development and increases the risk of addiction to other drugs. To combat this epidemic there are FDA approved nicotine cessation aids, however they are not effective in all individuals. One promising drug target is blockade of neurokinin 1 receptors (NK1Rs) to reduce nicotine consumption. Evidence exists that NK1Rs have the potential to alter nicotine consumption. NK1Rs antagonism modulates physical signs of nicotine withdrawal and can alter nicotineinduced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. My project is focused on testing the hypothesis that selective blockade of NK1Rs will reduce nicotine consumption in nicotine dependent mice. We will use the two-bottle choice paradigm to establish nicotine dependence and measure voluntary consumption of either a nicotine-containing solution or control solution. Mice will then be treated with the NKR antagonist L-732,138 to evaluate if NKR1s will reduce the consumption of nicotine. Our study will assess the potential of NK1Rs antagonism to be used as a new method to treat nicotine addiction.
-

Tracking Functional Connectivity using Dynamic Independent Component Analysis During the Meditative State
Aalliyah Celestine, Jeremy Cohen, and Wendy Hasenkamp
-

Ceramide Analog 315 and its Inhibitory Effects on Breast Cancer Tumor Growth
Degrick Cheatham, Camilla Do, Navneet Goyal, and Maryam Foroozesh
in women. Invasive breast cancer results in approximately 28% of all cancers diagnosed in the United States. This year, an estimated 276,480 women in the United States will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer. It is estimated that 42,690 deaths (42,170 women and 520 men) from breast cancer will occur this year. As a result, there is an urgent need for more effective and less toxic treatments for this devastating disease. Many anticancer drugs used to clinically treat cancers mediate tumor cell death through the induction of apoptosis. Cancer cells, however, often acquire resistance following prolonged exposure to clinical chemotherapeutic drugs. Consequently, molecular pathways involved in tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis have become potential targets for pharmacological intervention. Our group has targeted ceramide metabolism as a potential pharmacological intervention in the treatment of breast cancer. One novel approach is to synthesize ceramide analogs with greater efficacy and specificity than endogenous ceramides. Multiple families of ceramide analogs have been synthesized and evaluated in our previous studies leading to the current structure-activity relationship information. Analog 315 has been identified as the most promising analog. Analog 315 has proven to be less toxic and more effective than several previously studied ceramide analogs and will be used as a lead compound to synthesize additional ceramide analogs.
-

DESIGN AND SYNTHESIS OF NOVEL THERAPEUTIC AGENTS FOR VARIOUS FORMS OF BREAST CANCER
Holly Honore; Bouri Kang; and Honore, Dr. Bouri Kang, Dr. Florastina Payton-Stewart
The most frequently diagnosed cancer for women is breast cancer Around 5 10 of diagnosed breast cancer cases are metastatic and close to 30 of patients with early stage disease will go on to relapse with metastatic disease 1 Hormone receptor positive breast cancer makes up 70 of breast cancer cases The first line treatment for breast cancer is endocrine therapy Endocrine therapy, also known as hormone therapy, adds, blocks, or removes hormones to treat the disease There are two types of endocrine therapy for breast cancer One type is drugs that prevent estrogen and progesterone from being available for breast cancer cells to grow The other type of endocrine therapy is drugs or surgery to keep the ovaries from making hormones There are several different types of treatment options (see Figure 1 While we have made many advances in this area, a significant number of patients develop endocrine resistance, prompting the need for newer therapeutic agents 2
-

Design and Synthesis of Ck1δ and Ck1ε Inhibitors as Therapeutics for Alzheimer's Disease
Phong Huynh, Jayalakshmi Sridhar, and Linh Tran
The CK1 family of protein kinases are overexpressed in AD brains and have been linked with tau phosphorylation. For our study, we will be looking at two CK1 isoforms, CK1δ and CK1ε. Endogenous CK1δ greatly contributes to basal phosphorylation in the sample cells, while an overexpression of both isoforms saw a spike in tau phosphorylation. Previous studies have also shown that CK1δ can phosphorylate at least 15 sites in PHF-tau. We are trying to develop small-molecule kinase inhibitors that can better bind to tau protein than ATP, thereby reducing phosphorylation, maintaining cytoskeletal integrity, and stabilizing cell viability. Our research group has identified a series of compounds that function as ATP-competitive inhibitors of CK1d and CK1e. Docking studies are being performed for these compounds onto the X-ray crystal structure of CK1δ and CK1ε to understand the protein-inhibitor interactions. The results from the docking studies are presented here.
-

Assessing the Impact of a Nutritionally Complete Palatable Diet on Alcohol Dependence-induced Escalated Alcohol Drinking and Negative Emotional States in Male P-Rats
Larry Mason Jr., Joi Coleman, and Sunil Sirohi
-

Colorblind Racism and Identity Amongst College Students
Greg B. McCann-Smith
The purpose of this to study is to observe the changes in Black Identity and Colorblind Racism amongst black students following the murders of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor and Ahmaud Arbery. In 2019 I conducted an educational study that examined the relationship between Black Identity and Racial Colorblindness amongst college students within the psychology department. Although the purpose of that study was to determine a correlation between Black Identity and Racial Colorblindness, the data indicated that a substantial number of students scored high in Colorblind Racism and low on Black Identity. The data from the previous study will serve as preliminary data to conduct a comparative analysis of Black Identity and Colorblind Racism in response to current political climate. .
-
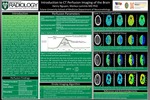
Introduction to CT Perfusion Imaging of the Brain.
Henry Nguyen and Markus Lammle
CT Perfusion (CTP) scanning of the brain is an essential part of the currently used diagnostic algorithm in the management of patients presenting with acute stroke. The current stroke imaging workup is initiated with a noncontrast head CT to rule out a possible hemorrhagic cause of the stroke symptoms or an intracranial hematoma which would represent a contraindication for intravenous lysis treatment. According to the current literature, CTP scans of the brain are of particular benefit for stroke patients arriving within 5-24 hours following the onset of symptoms or with unknown onset of symptoms such as wake-up strokes, which are unlikely to benefit from intravenous thrombolytic treatment, but will potentially benefit from intra-arterial thrombolysis or thrombectomy. CTP is used, ultimately to determine the total amount of ischemic cerebral tissue and to estimate the amount of salvageable cerebral tissue, to determine a potential benefit from endovascular therapy. The interpretation of CTP images is based on the evaluation of different perfusion parameter maps. The cerebral perfusion maps [1] include cerebral blood volume (CBV), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and perfusion delay maps, with mean transit time (MTT) and time to peak (TTP) maps most commonly used. A perfusion defect on CBV with perfusion defects matching in size and location on CBF and MTT or TTP maps indicate nonsalvageable cerebral tissue. In case of a normal CBV map, perfusion defects on MTT/TTP and CBF maps represent cerebral tissue at risk for infarct or salvageable cerebral tissue. Perfusion defects that are matching on all perfusion maps to include CBV are also referred to as core infarct i.e. non-salvageable tissue, as opposed to possible areas of salvageable cerebral tissue adjacent to the core infarct, called penumbra. Patients with a significant amount of penumbra with smaller core are candidates for endovascular therapy.
-

Design and Synthesis of Novel Therapeutic Agents for Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Deeuatrail Nichols Jr, Borui Kang, and Florastina Payton-Stewart
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is one of the rarest types of cancer present today. TNBC lacks the three most common types of receptors: HER2 (HER2-), estrogen receptors (ER-), and progesterone (PR-). This type of breast cancer affects only about 10% of breast cancer patients.Studies have also shown that TNBC primarily affects African-American and Hispanic women. Though many herapeutic drugs have been produced, many of them lack long-term potency. Research has shown that the phytochemical, berberine, possess anticancer properties. Berberine has shown to inhibit a wide range of cancer cell growth in cancer such as: melanoma, prostate, pancreatic,leukemia, and breast. The goal of our research is to synthesize analogs of berberine via Suzuki Coupling reactions. We will place various R groups on the C12 position of berberine. Previous studies have shown that the placing various R groups in the C12 position of berberine enhanced inhibition of breast cancer cells. Herein, we are proposing to synthesize analogs via Suzuki coupling and microwave chemistry. We hypothesize that our analogs of berberine will inhibit the growth of triple negative breast cancer cells in vitro superior to parental compound, berberine.
-

Design & Synthesis of Small Molecules as Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 2A6 for Tobacco Use Cessation
Chinyere Obioha, Camilla Do, Tulasi Ponnapakkam, Navneet Goyal, and Maryam Foroozesh
Cigarette smoking causes nearly one in every five deaths in the United States. The life expectancy of a smoker is 10 years less than a nonsmoker on average. Cigarette smoke contains more than 7,000 chemicals, seventy of which are known to cause cancer. Nicotine is responsible for the addictive and psychopharmacological effects of tobacco. Many tobacco components including nicotine are metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Nicotine is mainly metabolized by P450s 2A6 and 2A13. In this project, our goal is to design and synthesize selective metabolism-based inhibitors of P450 2A6. Such inhibitors can decrease the amount of tobacco chemicals metabolized into carcinogenic species. In addition, they can potentially be used for smoking cessation.
-

Using bis-MPA as a platform for novel drug delivery systems
Sharon Ogbonna, Blaine Derbigny, Greg Hodge, and Stassi DiMaggio
2,2-bis(methylol)propionic acid (bis-MPA) dendrimers are ideal backbones for novel drug delivery systems. Bis-MPA based dendrimers tend to be stable with multiple terminal groups with potential for functionalization, making them excellent for use in targeted drug delivery. However, these dendrimers have low water solubility. Amphiphilic block copolymers, a class of Stimuli Responsive Polymers (SRPs), can be conjugated to the end of the dendrimer. This increases the water solubility of the molecule while simultaneously increases the efficiency of SRPs. Water solubility can be further increased through the addition of polyethylene glycol (PEG) as linkages between the dendrimer and the SRP. The efficiency of free SRPs will be compared to the efficiency of the novel vehicle to determine if the proposed materials are viable as drug delivery systems.
-

Exosomes Influence TRAIL Expression in MCF-7 Estrogen Sensitive Breast Cancer Cells
Tresaundra M. Roberson, Jordon G. Coward, Kaitlyn S. Pekins, U’Ronnie Banks, Jasmine Johnson, and KiTani P. Lemieux
premenopausal African American and Hispanic women. Our group has taken an interest in nanosize membrane vesicles known as exosomes. We are particularly interested in the interaction that occurs between these exosomes and the tumor microenvironment, as it is believed that they promote proliferation, migration, and invasion. Therefore, we plan to evaluate the protein expression of TNFSF10 (TRAIL) in starved MCF-10A cells and the MCF-7 cell line. TRAIL is an apoptosis inducing ligand apart of the TNF superfamily. The MCF-7 cell line tends to be most insensitive to the TRAIL protein. In most cases cell lines are not sensitive to TRAIL because they lack the DR4 and/or DR5 receptors on their cell line surface or because they are deficient in caspase -8 and -3. The MCF-7 cell line contains both receptors, however they are deficient in both caspases. Therefore, we plan to evaluate the protein expression of TNFSF10 (TRAIL) in starved MCF-10A cells and the MCF-7 cell line. We plan to upregulate and down regulate TNFSF10 in the MCF-7 cell line to examine the functionality of the protein within the cell and tag our exosomes with TRAIL.
-

Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Ceramide Analogs
Karyn Wilson, Camilla Do, Tulasi Ponnapakkam, Navneet Goyal, and Maryam Foroozesh
Breast cancer is the most diagnosed form of cancer in women in the United States. It is estimated that on average, every two minutes a woman is diagnosed with breast cancer; and one woman will die of the disease every thirteen minutes. Many anti-cancer drugs used to clinically treat breast cancer mediate tumor cell death through the initiation of apoptosis. Multidrug-resistance is a major cause of cancer chemotherapy failure in clinical treatment. As a result, molecular pathways involved in tumor cell proliferation, including the ceramide signaling pathway, have become potential targets for pharmacological intervention. Ceramides have been shown to potentiate signaling events that drive apoptosis, autophagic responses, and cell cycle arrest. Ceramide analogs can be designed to inhibit ceramide-metabolizing enzymes in order to increase intra-cellular ceramide levels in cancer cells, leading to increased cell death. Our approach is to design and synthesize such ceramide analogs. Some of our synthesized analogs have been shown to have greater efficacy and specificity than endogenous ceramides. Evidence shows that multidrug-resistant cancer cells are as sensitive as corresponding regular cancer cells under the exposure to some of our anti-cancer ceramide analogs. Previously, a number of ceramide analogs with a flavone moiety on the backbone were synthesized. Initial docking studies showed that flavone moieties are too big for the binding pocket of human ceramidase. Coumarin-containing ceramide analogs, however, are smaller in size, and are expected to have increased efficiency along with self-fluorescence. For this project, new ceramide analogs containing a coumarin moiety on the sidechain were synthesized in order to study their biological activities.


